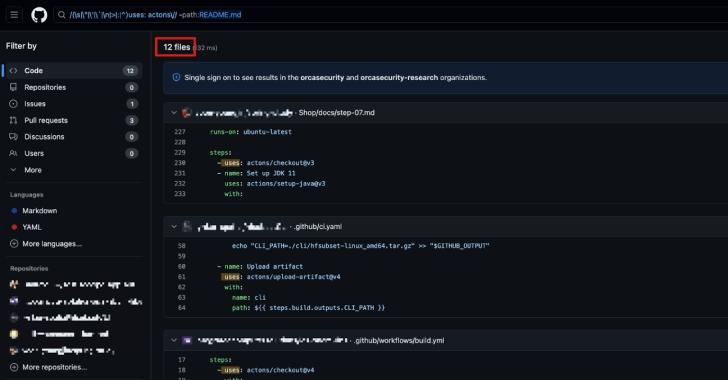
Threat actors have long leveraged typosquatting as a means to trick unsuspecting users into visiting malicious websites or downloading booby-trapped software and packages.
These attacks typically involve registering domains or packages with names slightly altered from their legitimate counterparts (e.g., goog1e.com vs. google.com).
Adversaries targeting open-source repositories across
Threat actors have long leveraged typosquatting as a means to trick unsuspecting users into visiting malicious websites or downloading booby-trapped software and packages.
These attacks typically involve registering domains or packages with names slightly altered from their legitimate counterparts (e.g., goog1e.com vs. google.com).
Adversaries targeting open-source repositories across